Integral
La integració és l’operació inversa de la derivació.
La integral d'una funció és l'àrea del gràfic de la funció.
Definició integral indefinida
Quan ![]()
Propietats integrals indefinides
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Variable de canvi d’integració
Quan![]() i
i![]()
![]()
Integració per parts
![]()
Taula d’integrals
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definició integral definida
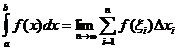
Quan![]()
![]()
![]()
Càlcul integral definit
Quan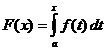 ,
,![]()
![]() i
i
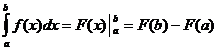
Propietats integrals definides
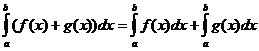
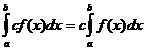
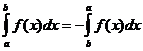
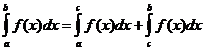
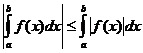
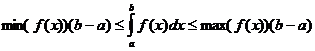 Quan
Quan![]()
Variable de canvi d’integració
Quan![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]()
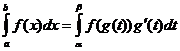
Integració per parts
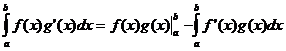
Teorema del valor mitjà
Quan f ( x ) és contínua hi ha un punt![]() tan
tan
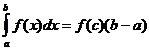
Aproximació trapezoïdal d’integral definit
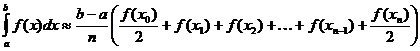
La funció gamma
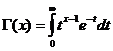
La funció Gamma és convergent per a x/ 0 .
Propietats de la funció gamma
G ( x +1) = x G ( x )
G ( n +1) = n ! , quan n ℕ (enter positiu).![]()
La funció beta
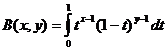
Funció beta i relació de la funció gamma
Advertising